Introduction
The healthcare industry stands at a fascinating crossroads. For decades, it has been characterized by deeply ingrained processes, regulatory complexities, and a paramount focus on patient well-being – all crucial, yet often acting as friction points against rapid innovation. While other sectors embraced digital transformation more swiftly, healthcare has traditionally taken a more cautious path, and for good reason. Lives are at stake, and any new technology must meet incredibly high standards of safety, accuracy, and compliance. But today, the urgency to modernize is no longer optional — it’s essential.
The convergence of rising patient expectations, increasing operational demands, and the transformative capabilities of digital technologies is forcing a shift. From AI-powered diagnostics and virtual care platforms to interoperable electronic health records and remote patient monitoring, digital tools are revolutionizing how care is delivered, accessed, and managed. These innovations promise not only improved efficiency and lower costs but also more personalized, proactive, and accessible healthcare for all. However, integrating these technologies into a complex and heavily regulated ecosystem remains a formidable challenge.
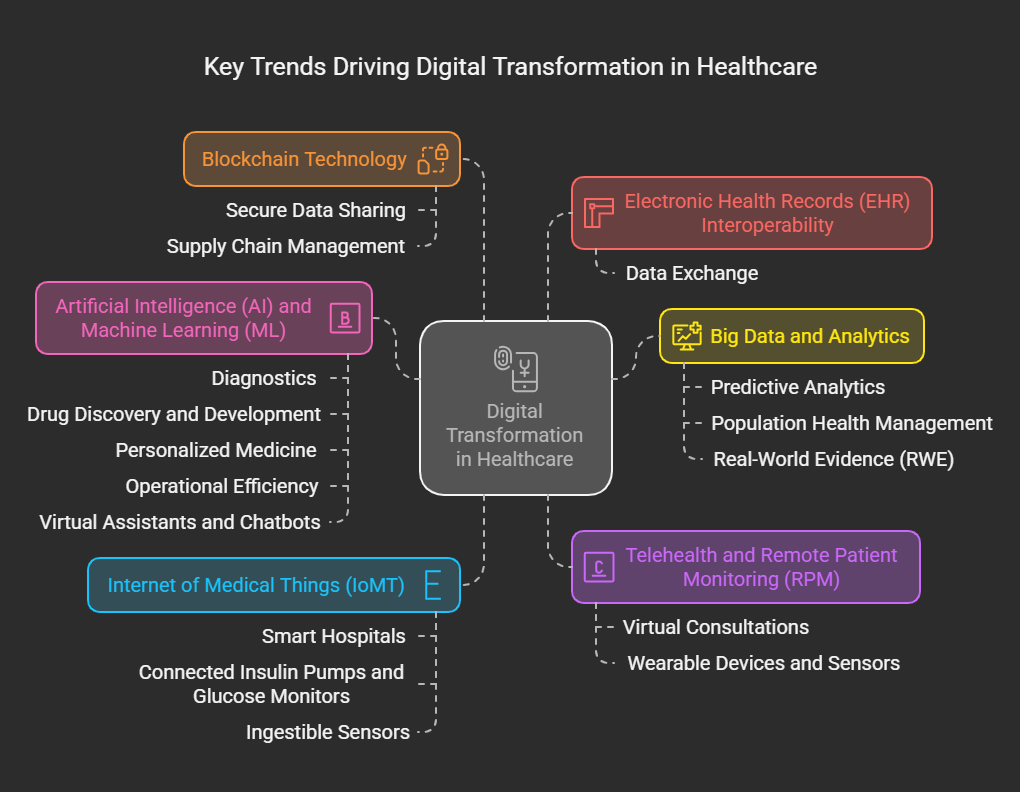
This post delves into the key trends shaping digital transformation in healthcare and examines the obstacles that the industry must address to fully realize its digitally empowered future. Several exciting trends are currently revolutionizing how healthcare is delivered and experienced, some of these trends are:
Key Trends: Healthcare
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and ML are poised to transform various aspects of healthcare.
- Diagnostics: Companies like Google Health are developing AI algorithms for early detection of diseases like cancer through medical imaging analysis. Start-ups like PathAI are using AI to improve the accuracy and speed of pathology diagnoses.
- Drug Discovery and Development: Pharmaceutical giants like Novartis and Pfizer are leveraging AI to accelerate the identification of potential drug candidates, predict clinical trial outcomes, and personalize treatment regimens.
- Personalized Medicine: AI algorithms can analyse vast datasets of patient information (genomics, lifestyle, medical history) to tailor treatments to individual needs. Companies like Tempus are focused on using genomic sequencing and AI to personalize cancer care.
- Operational Efficiency: AI-powered tools are being used for tasks like appointment scheduling, patient flow management, and automated administrative processes, freeing up healthcare professionals to focus on patient care.
- Virtual Assistants and Chatbots: Companies like Babylon Health offer AI-powered chatbots that can provide initial medical consultations, answer patient queries, and direct them to appropriate care pathways.
Telehealth and Remote Patient Monitoring (RPM)
The rise of telehealth has been accelerated by the need for remote care solutions.
- Virtual Consultations: Platforms like Teladoc Health and Amwell enable patients to connect with doctors and specialists remotely via video calls, expanding access to care, especially in underserved areas.
- Wearable Devices and Sensors: Companies like Fitbit and Apple (with Apple Watch) offer devices that can track vital signs (heart rate, sleep patterns, activity levels). When integrated with healthcare systems, these devices, along with specialized medical-grade sensors from companies like
- BioTelemetry, allow for continuous remote monitoring of patients with chronic conditions, enabling proactive interventions and reducing hospital readmissions.
Big Data and Analytics
The healthcare industry generates massive amounts of data. Harnessing this data effectively is crucial for improving outcomes and efficiency.
- Predictive Analytics: By analysing historical patient data, hospitals and healthcare systems can predict disease outbreaks, identify high-risk patients, and optimize resource allocation. Companies like Optum (part of UnitedHealth Group) offer advanced analytics solutions for healthcare organizations.
- Population Health Management: Analysing data across patient populations allows for the identification of health trends, the development of targeted interventions, and the improvement of overall community health.
- Real-World Evidence (RWE): Utilizing data from electronic health records (EHRs), insurance claims, and patient-generated data provides valuable insights into treatment effectiveness and patient outcomes in real-world settings.
Internet of Medical Things (IoMT)
The IoMT encompasses a network of connected medical devices and software applications that can collect, transmit, and analyse health data.
- Smart Hospitals: IoMT devices can automate tasks, monitor equipment, track assets, and improve patient safety within hospital environments.
- Connected Insulin Pumps and Glucose Monitors: Companies like Medtronic and Dexcom offer connected devices that allow for continuous glucose monitoring and automated insulin delivery for diabetes management.
- Ingestible Sensors: While still in early stages, companies are developing ingestible sensors that can monitor physiological parameters from within the body.
Blockchain Technology
While still relatively nascent in healthcare, blockchain offers potential for secure and transparent data management.
- Secure Data Sharing: Blockchain could enable patients to securely share their medical records with authorized providers, improving interoperability and reducing administrative burdens.
- Supply Chain Management: Blockchain can enhance the transparency and security of pharmaceutical supply chains, combating counterfeit drugs.
Electronic Health Records (EHR) Interoperability:
EHR systems are evolving to become more interoperable, allowing seamless patient data exchange across providers. This crucial development aims to break down data silos, providing a more holistic view of a patient’s medical history, reducing redundant tests, and improving care coordination. Initiatives and standards are being developed to facilitate this seamless exchange of information, ultimately leading to more informed clinical decision-making and enhanced patient safety.
Example of Healthcare firms
| Trend | Company | Initiative | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| AI & Machine Learning | Google Health / DeepMind | AI for disease detection (e.g., breast cancer, diabetic eye disease) | DeepMind Health |
| IBM Watson Health (Merative) | AI for clinical decision support & population health | IBM Watson Health (now Merative) | |
| Tempus | AI and data-driven precision medicine for cancer | Tempus Labs | |
| Telemedicine & Virtual Care | Teladoc Health | End-to-end virtual care platform | Teladoc Health |
| Amwell | Telehealth infrastructure for providers and payers | Amwell | |
| Amazon Clinic | Virtual care for common conditions via Amazon | Amazon Clinic | |
| EHR Interoperability | Epic Systems | “Open.epic” initiative for data sharing | Open.epic |
| Oracle Health (formerly Cerner) | Cloud-based, interoperable EHR solutions | Oracle Health | |
| Redox | API integration layer for health data exchange | Redox | |
| Health Gorilla | National Health Information Network (QHIN) | Health Gorilla | |
| Remote Patient Monitoring & Wearables | Apple | FDA-cleared ECG & health tracking via Apple Watch | Apple Health |
| Fitbit (Google) | Health monitoring, heart rhythm notifications | Fitbit Health Solutions | |
| Biofourmis | AI-powered remote patient monitoring platform | Biofourmis | |
| Philips | Enterprise-level RPM and telehealth systems | Philips RPM | |
| Blockchain in Healthcare | BurstIQ | Blockchain for secure health data exchange | BurstIQ |
| Guardtime Health | Health data integrity via blockchain | Guardtime Health | |
| IBM Blockchain | Blockchain solutions for medical records & supply chains | IBM Blockchain for Healthcare |
Challenges in DX for Healthcare
Despite the immense potential, several significant challenges hinder the widespread adoption of digital technologies in healthcare:
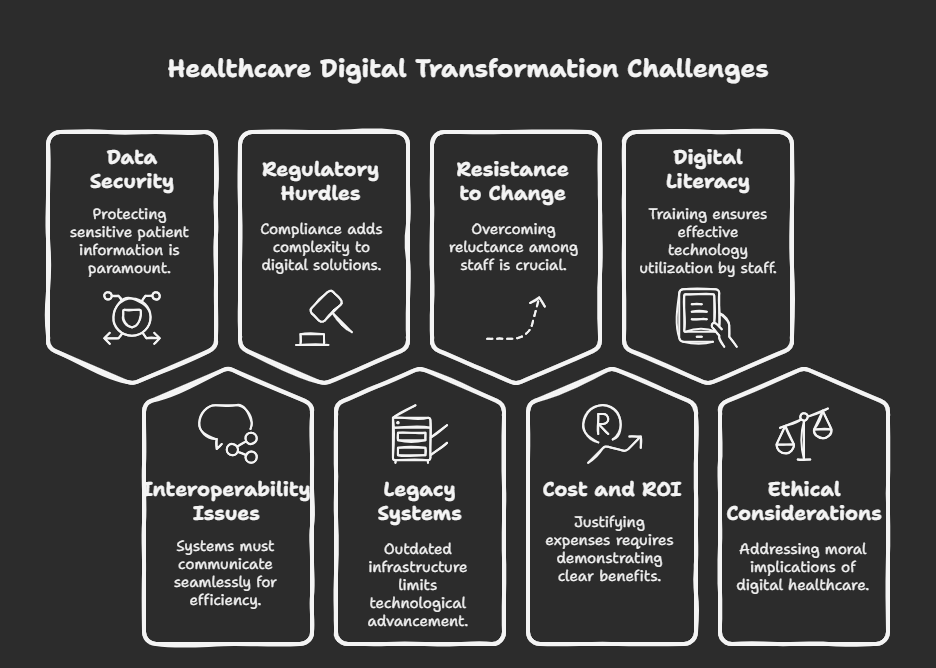
- Data Security and Privacy Concerns: The sensitive nature of patient health information makes data security and privacy paramount. Concerns about data breaches, misuse of data, and compliance with regulations like GDPR and HIPAA create significant barriers to adopting data-driven technologies. Building robust security infrastructure and ensuring patient trust are critical.
- Interoperability Issues: Healthcare systems often use disparate EHR systems and data formats, making it difficult to seamlessly exchange patient information. This lack of interoperability hinders the effective use of big data and AI, and can lead to inefficiencies and errors in patient care. Initiatives to standardize data formats and promote interoperability are crucial but face technical and organizational hurdles.
- Regulatory Hurdles: The healthcare industry is heavily regulated, and navigating the complex web of approvals and compliance requirements for new technologies can be time-consuming and expensive. Regulations often struggle to keep pace with the rapid advancements in digital health, creating uncertainty and slowing down adoption.
- Legacy Systems and Infrastructure: Many healthcare organizations still rely on outdated IT infrastructure that is not equipped to handle the demands of modern digital technologies. Upgrading or replacing these legacy systems requires significant investment and can disrupt existing workflows.
- Resistance to Change: Introducing new technologies often requires significant changes in workflows and processes, which can be met with resistance from healthcare professionals 1 who are accustomed to traditional 2 methods. Effective change management strategies, training, and demonstrating the benefits of these technologies are essential to overcome this resistance.
- Cost and Return on Investment (ROI): Implementing digital health solutions can involve significant upfront costs. Healthcare organizations need to see a clear return on investment, whether it’s through improved efficiency, better patient outcomes, or reduced costs in the long run. Demonstrating the economic value of digital transformation initiatives is crucial for securing buy-in.
- Digital Literacy and Skills Gap: Healthcare professionals need to be equipped with the necessary digital literacy and skills to effectively use new technologies. Training programs and ongoing support are essential to bridge this gap and ensure that technology is used effectively and efficiently.
- Ethical Considerations: The use of AI and big data in healthcare raises ethical concerns related to bias in algorithms, algorithmic transparency, and the potential for discrimination. Ensuring fairness, accountability, and transparency in the development and deployment of these technologies is crucial.
Conclusion
Digital transformation holds the key to a more efficient, personalized, and ultimately better healthcare future. The convergence of technologies like AI, telemedicine, big data, and IoMT is already reshaping how care is delivered and experienced—making it faster, more accessible, and increasingly proactive. These innovations not only improve operational efficiencies but also empower patients, placing them at the centre of their healthcare journeys. From real-time monitoring of chronic conditions to predictive analytics that anticipate outbreaks or hospital needs, the potential to save lives and improve quality of care is unprecedented.
However, realizing this potential requires more than just cutting-edge tools. The healthcare industry must proactively overcome deeply rooted challenges—such as fragmented data systems, stringent regulatory landscapes, cybersecurity vulnerabilities, and resistance to organizational change. True transformation will demand ongoing collaboration between technology innovators, healthcare providers, policymakers, and patients themselves. It will also require a cultural shift within institutions to embrace digital-first thinking, backed by strong governance and ethical safeguards.
By building bridges between these stakeholders and committing to thoughtful, inclusive implementation, the healthcare sector can fully harness the power of digital transformation. The result? A system that is not only smarter and more scalable, but also more humane—one that improves outcomes, reduces disparities, and creates lasting value for every patient, everywhere.
What is digital transformation in healthcare?
Digital transformation in healthcare refers to the integration of digital technologies—such as AI, telemedicine, IoT, and big data—into all areas of healthcare operations. It aims to improve patient care, streamline workflows, enhance diagnostics, and make healthcare more accessible and efficient.
What are the biggest challenges facing digital transformation in healthcare?
The key challenges include data privacy and security concerns, interoperability between systems, regulatory compliance, high implementation costs, and resistance to change within traditional healthcare structures.




