The world of customer service has undergone a dramatic transformation over the past few decades. To understand where we are heading with AI and chatbots, it’s important to look at how we got here.
Contact Centres: Birth and Evolution
Contact centers emerged in the 1960s and 1970s, with early examples like the Birmingham Press and Mail in the UK (credited with one of the first call centers in 1965) using private automated branch exchange (PABX) systems and answering machines to handle increasing customer inquiries. In the United States, airlines and telephone companies were among the pioneers adopting dedicated teams and technology to manage growing customer demands. Originally, these centers were on-shore, meaning they operated within the same country as the customer base. Staffed by local agents, they focused on answering calls, resolving issues, and tracking basic metrics like call duration and resolution times.
By the 1990s and early 2000s, globalization and cost pressures led many companies to shift contact center operations offshore. Countries like India, the Philippines, and Mexico became hubs for outsourced customer service. The goal was to reduce costs, scale operations, and handle growing call volumes while maintaining service quality.
The Journey: Metrics to Automation
I was part of the contact centre revolution which began in the early 2000s, where I was judged on hard metrics like: average handle time, first-call resolution, customer satisfaction scores, and call abandonment rates. However as digital transformation took hold, the scope expanded. Customers began expecting service across channels — not just phone, but email, chat, social media, and more.
Automation soon entered the picture. Interactive Voice Response (IVR) systems allowed callers to navigate menus without speaking to a human. Chatbots took this a step further, using scripted responses to answer common questions on websites or in apps. Robotic Process Automation (RPA) then helped automate back-end tasks, like processing refunds or updating account details, speeding up service delivery.
The Rise of AI
What has enabled this space to explode in recent years is the convergence of several forces: the rapid growth of digital communication channels (chat, email, social media), the democratization of cloud services, the rise of big data and machine learning, and customers’ rising expectations for instant, seamless support. These forces created a perfect storm where AI-driven tools — from chatbots to virtual agents — could be deployed at scale, transforming the customer service landscape almost overnight.
AI has elevated the game. Unlike rule-based bots, AI-driven chatbots leverage natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning to understand and respond to customer queries more intelligently. Virtual agents can now manage complex tasks, escalate issues when needed, and even detect customer sentiment.
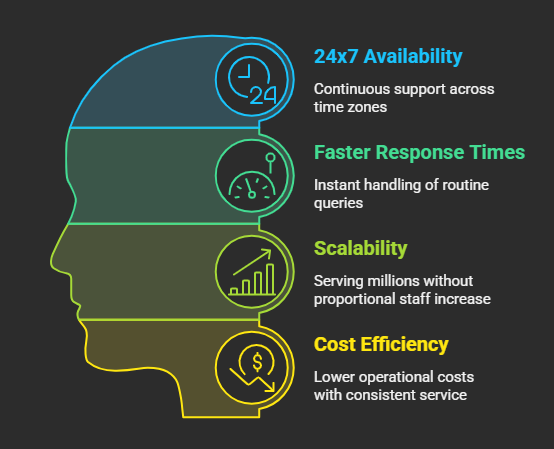
These changes have resulted in the following benefits for this industry:
- 24×7 availability: Customers can get support anytime, across time zones.
- Faster response times: AI handles routine queries instantly, reducing wait times.
- Scalability: Businesses can serve millions without proportional increases in human staff.
- Cost efficiency: Lower operational costs while improving service consistency.
Industries Adoption
Industries like banking, telecom, e-commerce, and travel are at the forefront, with companies like Amazon, Google, Salesforce, and IBM pushing AI-driven customer service innovations. Smaller startups are also emerging with specialized AI tools for niche customer service needs.
| Industry | Example Companies/Use Cases | Benefits Seen | Reference Link |
|---|---|---|---|
| Banking & Finance | Bank of America (Erica), Royal Bank of Canada (NOMI) | Faster inquiry handling, personalized insights, reduced workload | Fingent WotNot |
| Retail & E-commerce | Sephora (product recs on Messenger), Domino’s (Dom ordering bot) | Increased sales, improved shopping experience, faster orders | Fingent Rootstack |
| Healthcare | Zydus Hospitals (appointment chatbot), Babylon Health (symptom checker) | Automated bookings, 24/7 triage, improved patient access | WotNot EMA |
| Telecommunications | Deutsche Telekom (AI agents for HR and internal tasks) | Internal process automation, reduced employee query load | WSJ |
| Education | AI chatbots for student support, course enrollment, academic help (general) | Increased student engagement, 24/7 academic support | Valnox AI |
Fuelling AI Adoption
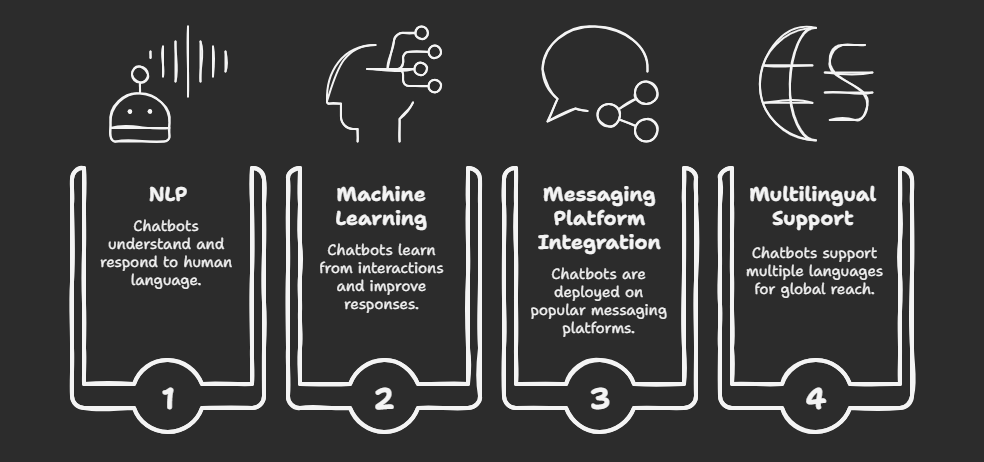
Several technological innovations have made chatbot deployment more accessible and effective. Natural Language Processing (NLP) allows chatbots to understand and interpret human language more naturally, while machine learning (ML) enables them to improve responses over time. Messaging platforms such as WhatsApp, Facebook Messenger, and Slack have provided a ready-made infrastructure to deploy chatbots where customers already are. Additionally, multilingual support has opened the door for companies to serve global audiences without needing large, multilingual human teams.
This wave of innovation has not only benefited large enterprises but has also lowered barriers for solo entrepreneurs and new-age companies. Today, even small businesses can integrate sophisticated chatbot solutions without massive investment, thanks to affordable cloud-based tools and APIs. These new business models are driving rapid adoption, as start-ups and small firms leverage AI to offer 24/7 customer service, scale operations, and compete effectively with established players.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP): Advancements in NLP enable chatbots to understand and respond to human language more effectively.
- Machine Learning: Allows chatbots to learn from interactions and improve over time, providing more accurate responses.
- Integration with Messaging Platforms: Deploying chatbots on platforms like WhatsApp and Facebook Messenger meets customers where they are, enhancing accessibility.
- Multilingual Capabilities: Supporting multiple languages expands the reach of chatbots to a global audience.
Impact on Humans?
A key question is: does this mean we no longer need humans in customer service? The short answer is no. While AI handles routine tasks, human agents are still critical for:
- Handling emotionally charged or sensitive interactions.
- Managing complex issues that require judgment, empathy, or negotiation.
- Overseeing and improving AI systems.
Instead of replacing humans, AI is reshaping roles. Agents are moving from script-following to higher-value activities: relationship management, product expertise, and continuous improvement of customer journeys.
Benefits of Human in the middle
While AI and automation are advancing fast, completely eliminating the need for humans in customer service is highly unlikely — at least in the foreseeable future.
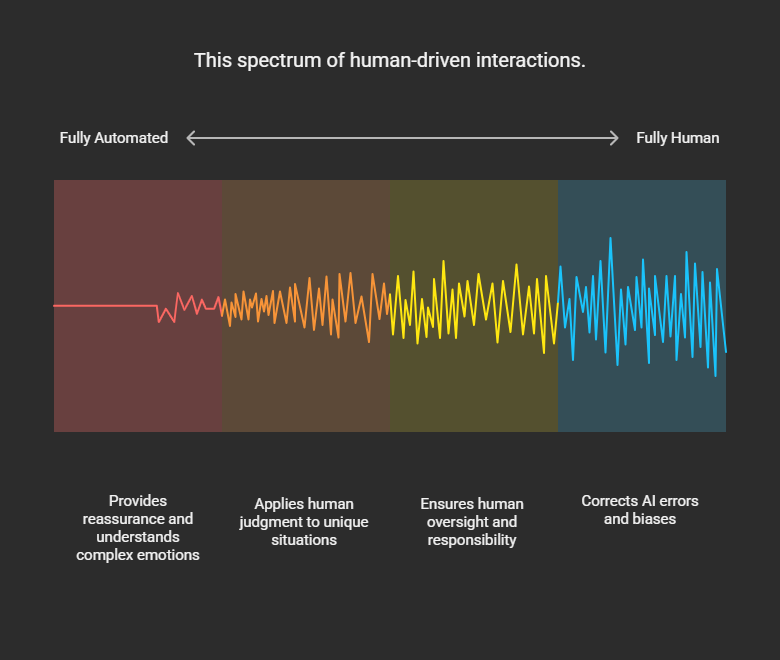
Human empathy & nuance:
AI can process language, but it still struggles with complex emotions, cultural context, ethical judgment, or subtle social cues. Angry, grieving, or sensitive customers often need human reassurance, not just factual responses.
Complex, non-standard cases:
Not all problems fit into scripts or predictable patterns. Edge cases, multi-layered disputes, legal issues, or unique customer circumstances often require human judgment.
Trust & accountability:
Many customers are uncomfortable with purely automated decisions, especially in industries like healthcare, finance, or law. They want to know a human is ultimately responsible and reachable.
AI limitations:
Even with large language models and advanced machine learning, AI can hallucinate (fabricate answers), misunderstand intent, or introduce biases from its training data — requiring human oversight and correction.
A Future Without Humans in Customer Service:
Imagine a world where no human agents are left in customer service. You call your bank, and an ultra-realistic AI voice greets you. It knows your entire financial history, predicts your needs, and handles complex transactions in seconds. You don’t speak to a person — ever.
You message a health chatbot about a strange symptom. The system, fed by billions of medical records, diagnoses you instantly, recommends treatment, and even schedules your prescription — no nurse, no doctor involved.
Your e-commerce complaints? Handled by an AI agent who scans your tone, calculates the best compensation to keep you loyal, and automatically refunds or replaces items — faster than any human ever could.
At first glance, this seems like a paradise of efficiency:
- No waiting on hold
- No human error or rudeness
- 24/7 service in any language
- Personalized, data-driven solutions at massive scale
What will be impact of this, do we want such a world where, we are missing out on Empathy and human connections, trust, accountability, displacement of workforce and ultimately are we going to be comfortable with algorithms deciding the outcome of people’s money, health, happiness without any intervention from humans?
Do We Want This Future?
The key question is not whether the technology can get there — it likely will. The deeper question is: should we allow AI to replace all human touch in industries that rely on trust, empathy, and accountability? Do we want a future where efficiency trumps humanity? Or should the goal be a balanced partnership: AI handling the routine, humans focusing on the meaningful?
Conclusion: Embracing AI with Caution
There’s no question that AI and chatbots are transforming customer service in extraordinary ways. They bring undeniable benefits: faster response times, 24/7 availability, cost savings, personalized experiences, and the ability to handle massive customer volumes without burnout. For businesses, this is a game-changer — unlocking efficiencies that were unimaginable just a decade ago.
But as we look ahead, we must also recognize the risks. A fully automated future raises serious concerns about empathy, fairness, accountability, privacy, and societal impact. Without careful design, AI could create systems that are fast and scalable — but cold, biased, and unaccountable.
How do we harness AI’s power without losing what makes customer service — and human interaction — truly meaningful?
To get the best of both worlds, companies and industries must approach AI adoption thoughtfully and responsibly. This means:
- Keeping humans in the loop for complex, emotional, or high-stakes interactions
- Designing robust guardrails that ensure AI systems are transparent, explainable, and auditable
- Regularly monitoring for bias, fairness, and unintended harms
- Prioritizing customer trust and consent, especially around data use
- Supporting workforce evolution, including reskilling and upskilling displaced employees
AI is not here to replace human connection — it’s here to enhance it. The challenge for the next 3–5 years isn’t just about scaling AI; it’s about scaling it wisely, with clear ethical boundaries and a commitment to keeping human values at the centre.
Will AI and chatbots completely replace human agents in customer service?
No. While AI can handle many routine and repetitive tasks, human agents are still essential for complex, emotional, or high-stakes interactions. The future will likely be a hybrid model where AI enhances human work rather than replaces it.
What are the key technologies driving chatbot adoption?
Technologies like Natural Language Processing (NLP), machine learning (ML), integration with messaging platforms (e.g., WhatsApp, Facebook Messenger), and multilingual support are making chatbots more accessible and effective across industries. These innovations lower costs and barriers, enabling even small businesses and solo entrepreneurs to deploy advanced customer service solutions.