Introduction
The Internet of Things (IoT) is driving a profound shift in the manufacturing sector by enabling smarter, more connected operations. Through the deployment of sensors, connected devices, and real-time analytics, manufacturers can now continuously monitor machine health, optimize energy usage, track inventory movement, and detect anomalies long before they lead to equipment failure. This level of visibility transforms static production environments into dynamic, self-aware ecosystems — resulting in reduced downtime, improved product quality, and higher overall operational efficiency.
In the age of Industry 4.0, IoT acts as the digital backbone that ties together various advanced technologies, including automation, machine learning, and digital twins. Manufacturers are using IoT to simulate entire production lines virtually, make faster decisions at the edge of the network, and personalize outputs with greater flexibility. Predictive analytics powered by IoT data allows teams to shift from reactive to proactive maintenance, minimizing costly disruptions. This convergence of physical assets with digital intelligence is what’s driving the rise of smart factories, capable of adjusting to real-time demands with minimal human intervention.
Beyond operational gains, IoT is reshaping long-term business models and competitiveness. Companies that embrace IoT-driven transformation can scale faster, customize products more easily, and deliver greater value to customers. However, success depends on having the right digital foundations — including scalable infrastructure, robust data governance, and agile processes. As global markets become more volatile and customer expectations continue to evolve, IoT empowers manufacturers to remain resilient, adaptive, and innovation-driven in an increasingly connected world.
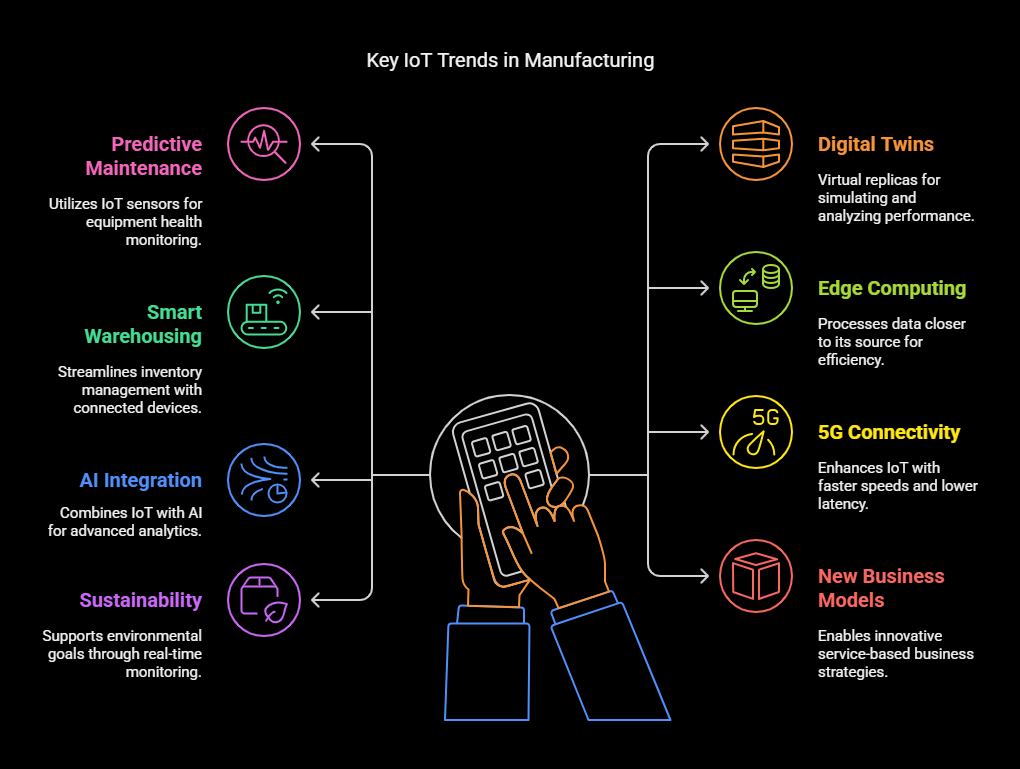
Key Trends in IoT
Predictive Maintenance
By utilizing IoT sensors to monitor equipment health in real-time, manufacturers can predict and prevent potential failures before they occur. This approach minimizes unplanned downtime and extends the lifespan of machinery. For instance, Texmark Chemicals implemented an IoT-enabled predictive maintenance system, resulting in improved operational efficiency and reduced maintenance costs.
Digital Twins
Digital twins are virtual replicas of physical assets or systems that allow manufacturers to simulate and analyse performance under various conditions. This technology aids in optimizing processes and product designs. Companies like BMW have employed digital twins to enhance factory operations and production line efficiency.
Smart Warehousing
IoT-driven smart warehouses utilize connected devices and automation to streamline inventory management and order fulfilment. Technologies such as RFID, autonomous robots, and drones facilitate real-time tracking and efficient handling of goods. Luxury fashion retailers like Harrods and Hugo Boss have invested in smart warehousing to enhance supply chain operations.
Edge Computing
Edge computing involves processing data closer to where it is generated, reducing latency and bandwidth use. In manufacturing, this means quicker decision-making on the factory floor, enhancing responsiveness and efficiency. The integration of edge computing with IoT devices is becoming increasingly prevalent in modern manufacturing setups.
AI Integration
Combining IoT with artificial intelligence (AI) enables advanced data analytics and automation. Manufacturers can leverage AI to analyse data collected from IoT devices, leading to insights that drive process improvements and innovation. ASUS IoT, for example, has developed AI-powered solutions to transform manufacturing processes.
5G and IoT Connectivity:
The rollout of 5G networks is revolutionizing IoT connectivity, providing faster speeds, lower latency, and increased bandwidth. This enhanced connectivity supports more complex IoT applications, enabling seamless data transfer and real-time communication between devices. IoT is used to enhance urban living through smart city projects. These projects use connected devices to manage traffic, energy consumption, and public safety. Singapore’s Smart Nation initiative uses IoT to improve urban planning and public services.
Sustainability and IoT:
IoT is playing an increasingly important role in sustainability efforts. By enabling real-time monitoring of energy consumption, waste management, and resource utilization, IoT solutions help businesses reduce their environmental footprint and achieve sustainability goals. For Example, IoT technologies have been integrated into waste management practices to enhance efficiency and sustainability. For instance, IoT-enabled systems can monitor waste levels in bins and optimize collection routes, leading to reduced fuel consumption and lower greenhouse gas emissions. A study demonstrated that such implementations resulted in a 20% reduction in overfilled trash cans and a 15% decrease in collection frequency, highlighting the environmental and operational benefits of IoT in waste management.
New Business Models
IoT enables the development of innovative business models, such as “product-as-a-service,” where businesses offer services based on the usage of their products. Example: Rolls-Royce’s “TotalCare” program uses IoT to monitor aircraft engines and provide predictive maintenance services, shifting from selling engines to selling engine uptime.
Additional Examples
| Example Application | Link | Key Benefit |
| GE Digital Predix | GE Digital Predix | Enhanced Operational Efficiency |
| Amazon Go | Amazon Go | Improved Customer Experience |
| IBM Supply Chain Insights | IBM Supply Chain Insights | Data-Driven Decision Making |
Key Challenges
While the Internet of Things (IoT) offers immense potential for transforming manufacturing, its adoption is not without challenges. Like any emerging technology, IoT brings a unique set of hurdles — from the complexity of implementation to concerns around data security, integration, and scalability.
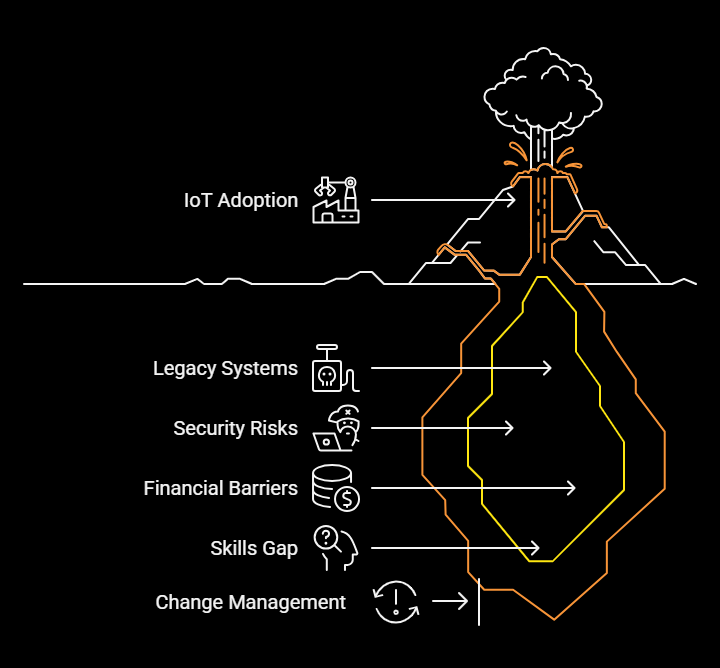
For many businesses, navigating these obstacles requires not only technical upgrades but also cultural and operational shifts. Below are some of the most common challenges companies face when implementing IoT solutions in industrial settings.
- Legacy Infrastructure
Many manufacturing facilities still rely on outdated machinery and control systems that lack IoT compatibility. Integrating new IoT-enabled technologies with legacy systems can be technically complex and costly.
- Data Security & Privacy
As more devices connect to the network, the attack surface expands. Manufacturers face significant concerns around securing sensitive operational data, protecting IP, and ensuring compliance with industry regulations.
- High Initial Investment
While IoT can yield strong ROI over time, the upfront costs of sensors, connectivity, integration, and training can deter small and mid-sized manufacturers from fully committing.
- Scalability & Standardization
With countless vendors and platforms in the IoT space, achieving seamless scalability and interoperability remains a challenge. Lack of standard protocols can hinder integration across different systems.
- Skills & Change Management
Implementing IoT requires new skill sets in data analytics, cloud computing, and cybersecurity. Businesses often struggle to find or upskill talent, and organizational resistance to change can further slow down adoption.
Conclusion
The role of IoT in business transformation is undeniable. By leveraging connected devices and data analytics, businesses can optimize operations, enhance customer experiences, and drive innovation. As technology continues to evolve, embracing IoT is crucial for staying ahead in the digital landscape.
Are you ready to harness the power of IoT for your business? Start by identifying key areas where IoT solutions can drive value, and explore partnerships with experienced IoT providers. Don’t let your business fall behind in the digital revolution. Begin your IoT journey today and unlock new opportunities for growth and success.
How is IoT transforming the manufacturing industry?
IoT is revolutionizing manufacturing by enabling real-time monitoring of equipment, predictive maintenance, energy optimization, and streamlined supply chains. It allows manufacturers to transition from reactive operations to proactive, data-driven decision-making — improving efficiency, reducing downtime, and boosting productivity.
What are the biggest challenges businesses face in adopting IoT?
Common challenges in IoT adoption include data security concerns, integration with legacy systems, lack of in-house expertise, high implementation costs, and ensuring scalable infrastructure. Overcoming these barriers often requires a clear strategy, investment in the right technology stack, and strong cross-functional collaboration.